Study Guide Notes For This Lesson
These are the words that are displayed and spoken during the lesson. Get these notes for the whole course in the Certification Study Guide, available in print or eBook. Many people tell us a printed companion book enhances their learning!
LANs for the most part run over cables inside buildings.
The term “cable” is often used to mean “bundles of wires”. Connectors or terminations may also be included in the package.
Copper wires are typically used for LAN cables. Copper is used because it is inexpensive, pliable, corrosion-resistant, and easy to extrude into long, thin wires.
Historically, copper wires have been used for two-wire telephone circuits (“loops”). The two wires are twisted together to reduce pickup of noise, and so are often referred to as twisted pair.
The wire may be solid or braided, the latter being more expensive to manufacture but better resistant to breakage.
A shield may be placed around individual pairs, and/or around the entire bundle of wires in a cable. The shield is a metal foil or mesh that prevents noise from reaching the wires inside it.
Category 5 and 5e cables, for up to 1 Gb/s are unshielded twisted pair (UTP). Category 6 cables have shielding as illustrated.
TIA-568 LAN Cable Categories
The most widely-followed standard for LAN cables is TIA-568, published by the Electronic Industries Association and its Telecommunications Industry Association sub-group.
This standard defines categories of twisted-pair cabling that support different line speeds.
Telecommunications Systems Bulletin TSB-67 adds the requirements and methods for field testing installed cable systems.
Taken together, these are the authority how to design and install a structured cabling system.
TIA-568 Category 1 cable is existing telephone cabling, also called Rusty Twisted Pair (RTP).
Category 2 cable was 25-pair multiconductor cables for old key telephone systems that had buttons to press to access different lines.
Category 3 cable was specified for 10 Mb/s Ethernet on twisted pair, 10BASE-T.
Category 4 cable was specified for the 16 Mb/s token ring.
Category 5 cabling was for the future at up to 1000 Mb/s.
All of these categories are now obsolete.
Cat 5 cable was supposed to handle Gigabit Ethernet, but in practice turned out to be missing the specification of required transmission characteristics.
Enhanced Category 5 (Cat 5e) was specified to guarantee the operation of 1000BASE-T.
Category 6 cable is specified to support 10 Gb/s on twisted pair. It starts being necessary to specify the frequency bandwidth supported on the twisted pair along with all of the other transmission characteristics to enable communication at these line speeds.
In theory, Category 7 supports 100 Gb/s on twisted pair.
This is the same bit rate as top-end fiber core network circuits, so one could probably expect it will be a while before we see any significant deployment of Cat 7.
Cable Construction
All of these categories specify cables with four pairs (eight wires) and a maximum length of 100 meters.
The difference between the categories rests in guaranteed transmission characteristics of the cable, including specifications for Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT), Attenuation to Crosstalk Ratio (ACR), supported frequency bandwidth, all of which affect the maximum possible information transfer rate, and hence what kind of devices can be successfully attached to each end of the cable.
One of the main factors in getting a cable certified to meet the TIA-568 category is quality control, particularly in the consistency of the twisting and placement of the pairs.
Two pairs will be twisted at a particular number of twists per inch, but offset by half a period to minimize crosstalk between the pairs.
The other two pairs will be twisted at a different rate that is not a multiple of the other, and similarly with the twists exactly not lined up.
How well and how consistently this is accomplished during the manufacturing process determines how successful the manufacturer will be in having the cable certified as meeting the standard.
Which to Use
When determining which category of cable to use, life cycle and cost are determining factors.
For a patch cable connecting a DSL or Cable Modem to a device inside a residence, where we have an expectation that the line speed will not exceed 100 Mb/s in the foreseeable future, then Cat 5 patch cables may be used.
For an extra ten cents, a Cat 5e patch cable would allow the continued use of the cable were the line speed to increase above 100 Mb/s, as it inevitably will at some time in the future.
When wiring a building, the cost of the labor to pull the cables is far more than the cost of the cable.
Conventional wisdom is to install the highest capacity available cable at the time the building is wired to avoid having to ever rewire the building.
The person who worked for a school board who got upset at me in a class for telling them they had made a mistake wiring their schools with Cat 3 to save a bit of money is to this day stuck at a maximum of 10 Mb/s, when the rest of the world is at 100 Mb/s and 1000 Mb/s.
At a minimum, Category 5e cable would be pulled in a building.
The smart money would install Category 6 certified cable terminated at one end on a Category 6 certified wall jack and at the other end on Category 6 certified patch panels.
Patch cords would then used to connect a computer’s LAN jack to the wall jack at one end, and from the patch panel to an Ethernet switch at the other end.
Ethernet switches are covered in an upcoming lesson.
Wiring Designs
The maximum run length of the cables – including runs through risers, poles, conduits – is 100 m (330 feet).
To be conservative, the patch panel and switch would be located in a wiring closet serving a radius of perhaps 100 feet.
These wiring closet switches could be connected to centralized Ethernet switches on each floor, which are connected to a switching router in the communications room, possibly using fiber.
A routing switch combines the functions of a LAN switch and router along with many other functions like DHCP.
In other cases, the wiring closet switches will be connected directly to a centralized switching router with regular LAN cables.
Since the labor cost is usually far greater than the cable, it is strongly recommended to install cable with capacity greater than immediate needs, and twice as many cables as what the conventional wisdom dictates.
Two Category 6 cables to each work area would be the Cadillac solution.
Two Category 5e cables to each work area would be well positioned for the future.
One Category 5 cable to each work area would probably be viewed as a mistake ten years down the road.














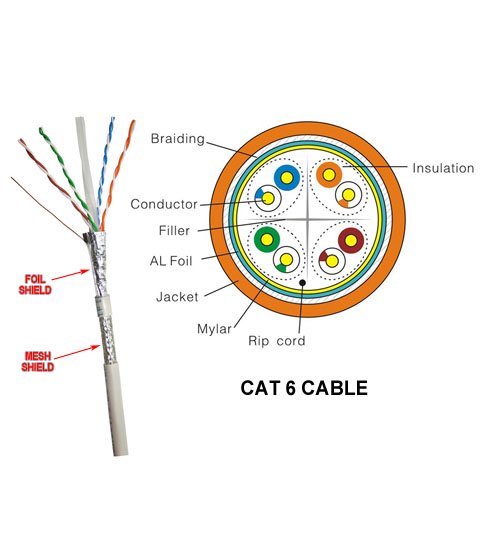 Cross-Section of TIA-568 Category 6 Cable
Cross-Section of TIA-568 Category 6 Cable 