One of the Holy Grails in the telecom business has always been the implementation of a converged network: a single network that supports all communications: telephone calls, television, video on demand, music, text, graphics, images, and anything else you can think of.
Initial attempts at a converged network using ATM and ISDN were unsuccessful and did not gain critical mass.
The third time proved to be the charm, and the converged telecom network is now a reality, using packets and packet switching following the IP set of standards.
IP is now an integral part of modern telecommunications, used in all parts of the network: the network core, access circuits and in-building. We call this IP Telecom.
Beginning with grunts and gestures, progressing to verbal messages, signal fires, written messages, postal services, telegraphy, radio, telephone, television and computer networks, each advance in technology has meant communication of more information, faster and to more people – but often with the need to adapt the information to suit the communication technology being used.
Realization of a converged network is another step in the evolution of the way humans communicate, in that communication mechanisms best suited to the information will be used, rather than the other way around.
The abbreviation "PSTN" has been a familiar part of the telecom lexicon for perhaps 100 years. Now its meaning is going to change.
For the past hundred years, PSTN has meant Public Switched Telephone Network:
- Public: Accessible to anyone who pays.
- Switched: A trunk switched onto the access lines at each end, for the duration of the call, then released.
- Telephone: Speaking at a distance.
- Network: Many interconnected nodes.
Going forward, "PSTN" will mean Packet-Switched Telecommunications Network:
- Packet-Switched: Communications in packets that are routed using IP managed with MPLS to the far end.
- Telecommunications: Transferring any kind of information across distance.
- Network: Many interconnected nodes.
It may be necessary to call this the IP-PSTN for a transitional period, until trunks and circuit-switching falls into the same dustbin of history as step-by-step switches.
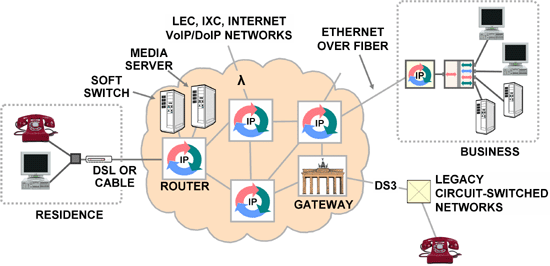
The basic telecom service is IP dial tone: high bit-rate access circuits and the possibility of communicating IP packets to any point on the network. “Businesses” (including government, educational institutions and the like) will use Ethernet over fiber at Gigabit speeds for access. Residences not yet served by fiber will use modems over copper wires – either DSL or cable for quite some time to come.
Many different kinds of value-added services will be available in addition to basic IP dial tone, some of them provided by the same company that provides the dial tone, others provided by third parties.
The lowest level of value-added services includes service level agreements and network and information security services. An unending list of higher-level services will be available for use on the network; some free, many not. Telephone service, television, Internet, radio, videophones, texting, desktop sharing, and integrated email/voicemail messaging are easy examples.
DMS-100 and 5ESS switches will be replaced with softswitches – software on servers on the IP network. Media servers support voicemail and video programming. Internet service will become simply a few ancillary services such as a Domain Name Server and an outgoing email server; the capability to communicate with web servers will be part of the dial tone.
This is the biggest change in telecommunications since the invention of the telephone switch… certainly more important than the change from analog to digital transmission in the 1980s, and it will have a profound impact on the way people communicate.
Take BOOT CAMP to get up to speed on the new IP Telecom.
Fill in the gaps, bust the buzzwords, demystify the jargon and understand the technologies like fiber, wireless, Ethernet, MAC frames, IP packets, MPLS - and how it all fits together, in plain English.
Be more effective, more confident and less frustrated with jargon by understanding the fundamentals
... career-enhancing foundational knowledge that lasts a lifetime.









