- Rings around town
- Regional rings
- Multiple interconnections
- OC192
=192 DS3
=129,024 DSOs
=10 Gb/s line speed
- Multiple colors of light: 30 to 300 per fiber @ multiple fibers per cable
- 100 million+ DS0s/cable
- Terabits per second
Fiber is a physical medium on which we can represent bits, just as copper is. Fiber is used as the basis of connections between switching and routing centers since it can support very high numbers of bits per second. These kind of connections are often referred to as the backbone of a network. Lower-speed (and lower-cost) circuits are used to provide access to this backbone to users.
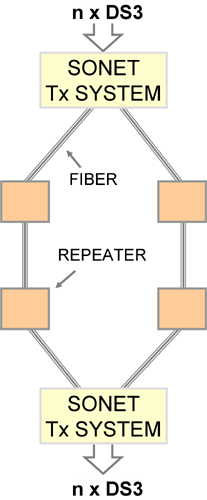
We need a method of organizing the bits on a fiber, and methods of alarming, automatic switching to backup and capacity management. Before about year 2000, the most popular technology for these functions was a standard called Synchronous Optical Network (SONET).
SONET is now considered a legacy technology; all new builds use Optical Ethernet. But that does not mean that SONET no longer exists... there are thousands and thousands of SONET systems still in operation.
SONET usually employs the Optical Carrier system. The Optical Carrier is a method of transporting multiple DS3-rate signals on fiber. Compare this to the T1 Carrier which is a method of transporting DS1-rate signals on copper wires. Like T1, OC also uses time division multiplexing, framing bits and so forth.
A hierarchy of OC rates is established. An OC1 carries 1 DS3, an OC3 carries 3 DS3, and so forth. OC48 systems have been widely deployed. OC48 carries 48 DS3-rate signals, which equals 32,256 DS0 signals, on a single fiber. This is around 2.1 x 109 b/s = 2.1 Gb/s. Additional bits for framing, signaling and control are added. These extra bits are usually called overhead and increase the total line speed of an OC48 system to about 2.5 Gb/s. OC192 systems are now being deployed. These carry a payload of 192 DS3-rate signals (129,024 DS0 channels) plus overhead.
To ensure high availability, that is, the possibility of communicating even if a line is cut, we need to provide multiple redundant paths between each point. The cheapest way to do this is to connect locations together in ring patterns. This way, there are two connections to every location, but only one extra circuit. SONET rings are used to connect COs in a city together. SONET rings are also installed to connect cities in regions together, and these regional rings are interconnected at multiple places for long-distance communications.
A significant advance in fiber optic technology is called Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM) or Dense Wave Division Multiplexing (DWDM). These terms refer to the technique of using multiple colors of light (called carriers or wavelengths in the optical business) on the same fiber. Current technologies allow for hundreds of wavelengths on a single fiber, each representing a different OC192. With multiple fibers in a cable, each with multiple OC192s, we end up with transmission systems moving hundreds of millions of DS0 channels: bit rates measured in Terabits per second.
This was the basis of what was called the "Information Superhighway" in the 1980s and 1990s. (Called the Internet today).
Going forward, Optical Ethernet technology is used for all new installations, for both transmission and access circuits. This achieves two the long-time goals in the telecom business: the same technology used in all parts of the network, that can be scaled to arbitrarily high line speeds.
In the not-too-distant future, 10 Gb/s will be a common access speed to the backbone. People used to think 1.5 Mb/s was fast.









